CSS3与页面布局学习总结系之一 —— 概要、选择器、特殊性与刻度单位
此系列文章为转载文章,原出完整系列已经不从考证。从不同地方摘录到此,以备阅读方便,特此记录。
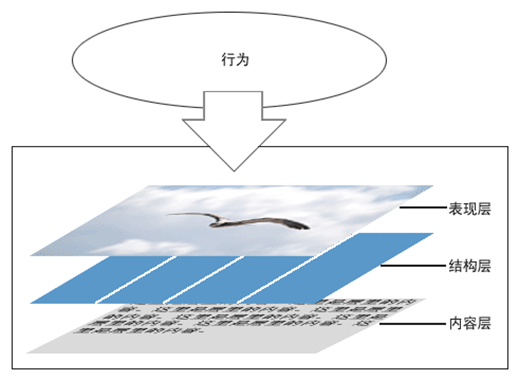
web前端开发者最最注的内容是三个:HTML、CSS与JavaScript,他们分别在不同方面发挥自己的作用,HTML实现页面结构,CSS完成页面的表现与风格,JavaScript实现一些客户端的功能与业务。当然内容与用户资源也是不能忽视的。尽量不要跨职责范围使用,有点“SRP单一职责”的意思,如字体大小应该是CSS控制的,就不应该使用HTML标签完成,如果CSS能解决的问题尽量不要用JavaScript完成。
CSS3 概要
CSS(Cascading Style Sheet)是层叠样式表的意思,CSS3就是在CSS2.1的基础上升级的CSS新版本,属于HTML5的一部分。它可以有效地对页面的布局、字体、颜色、背景、动画和其它效果实现。CSS3是CSS技术的升级版本,CSS3语言开发是朝着模块化发展的。以前的规范作为一个模块实在是太庞大而且比较复杂,所以,把它分解为一些小的模块,更多新的模块也被加入进来。这些模块包括: 盒子模型、列表模块、超链接方式 、语言模块 、背景和边框 、文字特效 、多栏布局等。

-
特点
-
效果演示
纯 CSS3 画出小黄人并实现动画效果
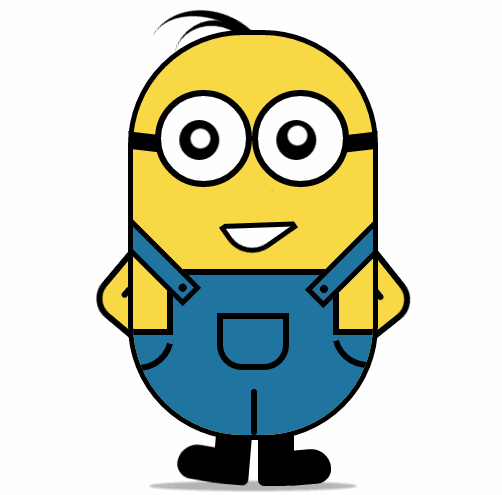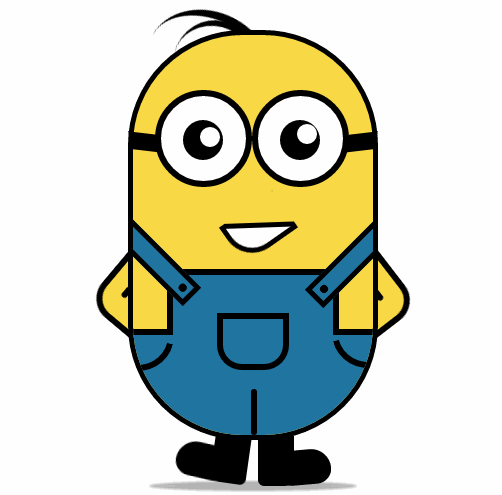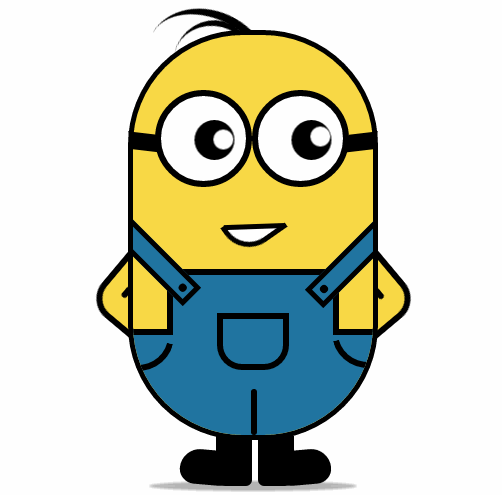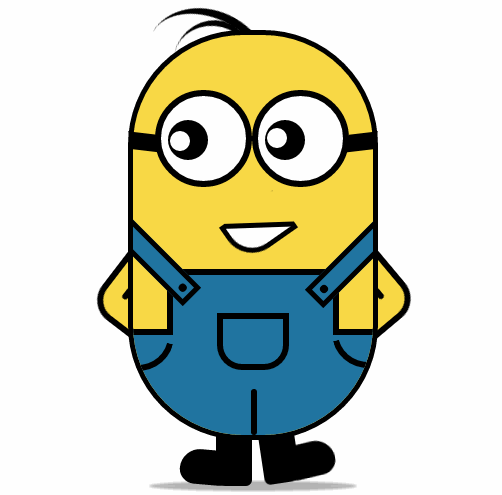
-
源码
HTML 源码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>drawLittleHuang</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="drawLittleHuang.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper"><!-- 容器 -->
<div class="littleH"><!-- 小黄人 -->
<div class="bodyH"><!-- 身体 -->
<div class="trousers"><!-- 裤子 -->
<div class="condoleBelt"><!-- 吊带 -->
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
<div class="trousers_top"></div><!-- 裤子突出的矩形部 分 -->
<div class="pocket"></div><!-- 裤袋 -->
<!-- 三条线 -->
<span class="line_left"></span>
<span class="line_right"></span>
<span class="line_bottom"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="hair"><!-- 头发 -->
<span class="left_hair_one"></span>
<span class="left_hair_two"></span>
</div>
<div class="eyes"><!-- 眼睛 -->
<div class="leftEye"><!-- 左眼 -->
<div class="left_blackEye">
<div class="left_white"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="rightEye"><!-- 右眼 -->
<div class="right_blackEye">
<div class="right_white"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="mouse"><!-- 嘴巴 -->
<div class="mouse_shape"></div>
</div>
<div class="hands"><!-- 双手 -->
<div class="leftHand"></div>
<div class="rightHand"></div>
</div>
<div class="feet"><!-- 双脚 -->
<div class="left_foot"></div>
<div class="right_foot"></div>
</div>
<div class="groundShadow"></div><!-- 脚底阴影 -->
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>CSS3 源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405@charset "utf-8";
body{
margin: 0;
padding:0;
}
.wrapper{
width: 300px;
margin:100px auto;
}
.litteH{
position: relative;
}
.bodyH{
position: absolute;
width: 240px;
height: 400px;
border:5px solid #000;
border-radius: 115px;
background: rgb(249,217,70);
overflow: hidden;
z-index: 2;
}
.bodyH .condoleBelt{
position: absolute;
}
.bodyH .condoleBelt .left,
.bodyH .condoleBelt .right{
width: 100px;
height: 16px;
border:5px solid #000;
background: rgb(32,116,160);
position: absolute;
top:-90px;
left:-35px;
z-index: 2;
-webkit-transform:rotate(45deg);
}
.bodyH .condoleBelt .left{
top:-88px;
left:165px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(-45deg);
}
.bodyH .condoleBelt .left:after,
.bodyH .condoleBelt .right:after{
content: '';
width: 8px;
height: 8px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #000;
position: absolute;
top:4px;
left:88px;
}
.bodyH .condoleBelt .left:after{
left:5px;
}
.bodyH .trousers{
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
border-top: 6px solid #000;
background: rgb(32,116,160);
}
.trousers_top{
width: 160px;
height: 60px;
border:6px solid #000;
border-bottom: none;
border-radius: 0 0 5px 5px;
background: rgb(32,116,160);
position: absolute;
bottom: 100px;
left:34px;
}
.pocket{
width: 60px;
height: 45px;
border:6px solid #000;
border-radius: 0px 0px 25px 25px;
position: absolute;
bottom:65px;
left:84px;
}
.line_right{
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 100px;
border-bottom:6px solid #000;
border-left:6px solid #000;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
bottom:60px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(-75deg);
}
.line_left{
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 100px;
border-bottom:6px solid #000;
border-right:6px solid #000;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
bottom:63px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(75deg);
}
.line_bottom{
height: 40px;
border:3px solid #000;
border-radius: 3px;
position: absolute;
left:118px;
bottom: 0px;
}
.hair{
position: relative;
}
.left_hair_one{
width: 130px;
height: 100px;
border-radius: 50%;
border-top:8px solid #000;
position: absolute;
left:17px;
top:-17px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(27deg);
-webkit-animation: lefthair 2s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes lefthair{
0%,25%,31%,100%{
}
30%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(31deg) translate3d(-3px,-1px,0);
}
}
.left_hair_two{
width: 80px;
height: 80px;
border-radius: 50%;
border-top:6px solid #000;
position: absolute;
left:45px;
top:-10px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(15deg);
}
.eyes{
position: relative;
z-index: 3;
}
.eyes .leftEye,.eyes .rightEye{
width: 85px;
height: 85px;
border-radius: 50%;
border:6px solid #000;
background: #fff;
position: absolute;
top:60px;
left: 27px;
}
.eyes .leftEye{
left: 124px;
}
.eyes .leftEye .left_blackEye,
.eyes .rightEye .right_blackEye{
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #000;
position: absolute;
top:24px;
left:22px;
-webkit-animation: blackeye 5s ease-in infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes blackeye{
0%,20%,50%,70%,100%{
-webkit-transform: translateX(0px);
}
30%,40%{
-webkit-transform: translateX(15px);
}
80%,90%{
-webkit-transform: translateX(-15px);
}
}
.eyes .leftEye .left_blackEye .left_white,
.eyes .rightEye .right_blackEye .right_white{
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #fff;
position: absolute;
top:7px;
left:17px;
-webkit-animation: whiteeye 5s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes whiteeye{
0%,20%,50%,70%,100%{
-webkit-transform: translateX(0px);
}
30%,40%{
-webkit-transform: translate3d(3px,4px,0);
}
80%,90%{
-webkit-transform: translate3d(-15px,4px,0);
}
}
.eyes .leftEye .left_blackEye .left_white{
top:4px;
left:17px;
}
.eyes .leftEye:after,
.eyes .rightEye:after{
content: '';
width: 28px;
height: 18px;
background: #000;
position: absolute;
left:-30px;
top:37px;
-webkit-transform:skewX(20deg) rotate(7deg);
}
.eyes .leftEye:after{
left:89px;
top:37px;
-webkit-transform:skewX(-20deg) rotate(-7deg);
}
.mouse{
position: relative;
}
.mouse .mouse_shape{
width: 55px;
height: 35px;
border:5px solid #000;
border-bottom-left-radius: 30px;
background: #fff;
position: absolute;
top:175px;
left:98px;
z-index: 3;
-webkit-transform:rotate(-35deg);
-webkit-animation: mouse 5s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes mouse{
40%,43%{
width: 45px;
height: 25px;
top:180px;
}
0%,35%,48%,100%{
width: 55px;
height: 35px;
top:175px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(-35deg);
}
}
.mouse .mouse_shape:after{
content: '';
width: 70px;
height: 32px;
border-bottom:5px solid #000;
border-radius:35px 26px 5px 5px;
background: rgb(249,217,70);
position: absolute;
top:-16px;
left:3px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(34deg);
-webkit-animation: mouse_mask 5s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes mouse_mask{
40%,43%{
width: 60.5px;
top:-19.3px;
left:1.5px;
}
0%,35%,48%,100%{
width: 70px;
top:-16px;
left:3px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(33deg);
}
}
.hands{
position: relative;
}
.hands .leftHand,
.hands .rightHand{
width: 80px;
height: 80px;
border:6px solid #000;
border-radius: 25px;
background: rgb(249,217,70);
position: absolute;
top:220px;
left:-23px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(40deg);
-webkit-animation:rightHand .8s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes rightHand{
0%,50%,100%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(40deg);
}
30%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(37deg) translateX(1px);
}
}
.hands .leftHand{
left:182px;
top:220px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(-40deg);
-webkit-animation:leftHand .8s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes leftHand{
0%,50%,100%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(-40deg);
}
80%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(-37deg) translateX(-1px);
}
}
.hands .leftHand:after,
.hands .rightHand:after{
content: '';
width: 6px;
border:3px solid #000;
border-radius: 3px;
position: absolute;
left:13px;
top:50px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(90deg);
}
.hands .leftHand:after{
left:53px;
top:50px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(-90deg);
}
.feet{
position: relative;
}
.feet .left_foot,
.feet .right_foot{
width: 36px;
height: 50px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 6px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 9px;
background: #000;
position: absolute;
top: 406px;
left:88px;
-webkit-transform-origin: right top;
-webkit-animation: rightfoot .8s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes rightfoot{
0%,50%,100%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(0deg);
}
80%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(10deg);
}
}
.feet .left_foot{
border-bottom-right-radius: 9px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 6px;
left:130px;
-webkit-transform-origin: left top;
-webkit-animation: leftfoot .8s ease-in-out infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes leftfoot{
0%,50%,100%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(0deg);
}
30%{
-webkit-transform: rotate(-10deg);
}
}
.feet .left_foot:after,
.feet .right_foot:after{
content: '';
width: 60px;
height: 35px;
border-radius: 20px 10px 21px 15px;
background: #000;
position: absolute;
left:-36px;
top:14.4px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(5deg);
}
.feet .left_foot:after{
border-radius: 10px 20px 15px 21px;
left:13px;
-webkit-transform:rotate(-5deg);
}
.groundShadow{
width: 200px;
height: 2px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: rgba(0,0,0,0.3);
box-shadow: 0 0 2px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.3);
position: relative;
top: 455px;
left:25px;
} -
帮助文档与学习
-
权威的帮助文档是最好的学习资料,CSS2 的帮助,非常详细:
-
CSS3的帮助文档:

如果打开时右边全是空白,请右键->“属性”—>“解除锁定”
选择器
常用选择器
在使用CSS时我们首先要做的事情是找到元素,在写相应的样式,在CSS2.1中最常使用的是三种选择器:
-
ID选择器:以#开始,引用时使用id,如id=“div1”
1
2
3
4#div1
{
color:red;
} -
类选择器:以.开始,使用class属性引用,可以有多个,如class=“cls1 cls2 cls3”
1
2
3
4.cls1
{
background-color:#99ccff;
}备注:class中出现多个值的时候,不以值在class中出现的先后顺序判断,而是以定义时的先后,就近原则,例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<style type="text/css">
.red {
color: red;
}
.green {
color: green;
}
.blue {
color: blue;
}
</style>
<!-- 此处Hello CSS3!颜色为 blue-->
<h2 class="red blue green">Hello CSS3!</h2>
</body>
</html>显示结果为:

-
标签选择器:以标签名称开始,如
p,span,div,*1
2
3
4div span
{
font-size:14px;
}
当然还有如伪类选择,a:hover,a:link,a:visted,a:active。
在CSS3中新增了很多的选择器,如果大家会 jQuery,jQuery 中多数选择器在 CSS3 中都可以直接使用。
| 选择器 | 例子 | 例子描述 | CSS 版本 |
|---|---|---|---|
| .class | .intro | 选择 class=“intro” 的所有元素。 | 1 |
| #id | #firstname | 选择 id=“firstname” 的所有元素。 | 1 |
| * | * | 选择所有元素。 | 2 |
| element | p | 选择所有 <p> 元素。 | 1 |
| element,element | div,p | 选择所有 <div> 元素和所有 <p> 元素。 | 1 |
| element element | div p | 选择 <div> 元素内部的所有 <p> 元素。 | 1 |
| element>element | div>p | 选择父元素为 <div> 元素的所有 <p> 元素。 | 2 |
| element+element | div p | 选择紧接在 <div> 元素之后的所有 <p> 元素。 | 2 |
| [attribute] | [target] | 选择带有 target 属性所有元素。 | 2 |
| [attribute=value] | [target=_blank] | 选择 target=“_blank” 的所有元素。 | 2 |
| [attribute~=value] | [title~=flower] | 选择 title 属性包含单词 “flower” 的所有元素。 | 2 |
| [attribute|=value] | [lang|=en] | 选择 lang 属性值以 “en” 开头的所有元素。 | 2 |
| :link | a:link | 选择所有未被访问的链接。 | 1 |
| :visited | a:visited | 选择所有已被访问的链接。 | 1 |
| :active | a:active | 选择活动链接。 | 1 |
| :hover | a:hover | 选择鼠标指针位于其上的链接。 | 1 |
| :focus | input:focus | 选择获得焦点的 input 元素。 | 2 |
| :first-letter | p:first-letter | 选择每个 <p> 元素的首字母。 | 1 |
| :first-line | p:first-line | 选择每个 <p> 元素的首行。 | 1 |
| :first-child | p:first-child | 选择属于父元素的第一个子元素的每个 <p> 元素。 | 2 |
| :before | p:before | 在每个 <p> 元素的内容之前插入内容。 | 2 |
| :after | p:after | 在每个 <p> 元素的内容之后插入内容。 | 2 |
| :lang(language) | p:lang(it) | 选择带有以 “it” 开头的 lang 属性值的每个 <p> 元素。 | 2 |
| element1~element2 | p~ul | 选择前面有 <p> 元素的每个 <ul> 元素。 | 3 |
| [attribute^=value] | a[src^=“https”] | 选择其 src 属性值以 “https” 开头的每个 <a> 元素。 | 3 |
| [attribute$=value] | a[src$=“.pdf”] | 选择其 src 属性以 “.pdf” 结尾的所有 <a> 元素。 | 3 |
| [attribute*=value] | a[src*=“abc”] | 选择其 src 属性中包含 “abc” 子串的每个 <a> 元素。 | 3 |
| :first-of-type | p:first-of-type | 选择属于其父元素的首个 <p> 元素的每个 <p> 元素。 | 3 |
| :last-of-type | p:last-of-type | 选择属于其父元素的最后 <p> 元素的每个 <p> 元素。 | 3 |
| :only-of-type | p:only-of-type | 选择属于其父元素唯一的 <p> 元素的每个 <p> 元素。 | 3 |
| :only-child | p:only-child | 选择属于其父元素的唯一子元素的每个 <p> 元素。 | 3 |
| :nth-child(n) | p:nth-child(2) | 选择属于其父元素的第二个子元素的每个 <p> 元素。 | 3 |
| :nth-last-child(n) | p:nth-last-child(2) | 同上,从最后一个子元素开始计数。 | 3 |
| :nth-of-type(n) | p:nth-of-type(2) | 选择属于其父元素第二个 <p> 元素的每个 <p> 元素。 | 3 |
| nth-last-of-type(n) | p:nth-last-of-type(2) | 同上,但是从最后一个子元素开始计数。 | 3 |
| :last-child | p:last-child | 选择属于其父元素最后一个子元素每个 <p> 元素。 | 3 |
| :root | :root | 选择文档的根元素。 | 3 |
| :empty | p:empty | 选择没有子元素的每个 <p> 元素(包括文本节点)。 | 3 |
| :target | #news:target | 选择当前活动的 #news 元素。 | 3 |
| :enabled | input:enabled | 选择每个启用的 <input> 元素。 | 3 |
| :disabled | input:disabled | 选择每个禁用的 <input> 元素 | 3 |
| :checked | input:checked | 选择每个被选中的 <input> 元素。 | 3 |
| :not(selector) | :not(p) | 选择非 <p> 元素的每个元素。 | 3 |
| ::selection | ::selection | 选择被用户选取的元素部分。 | 3 |
选择器分类
-
基础的选择器
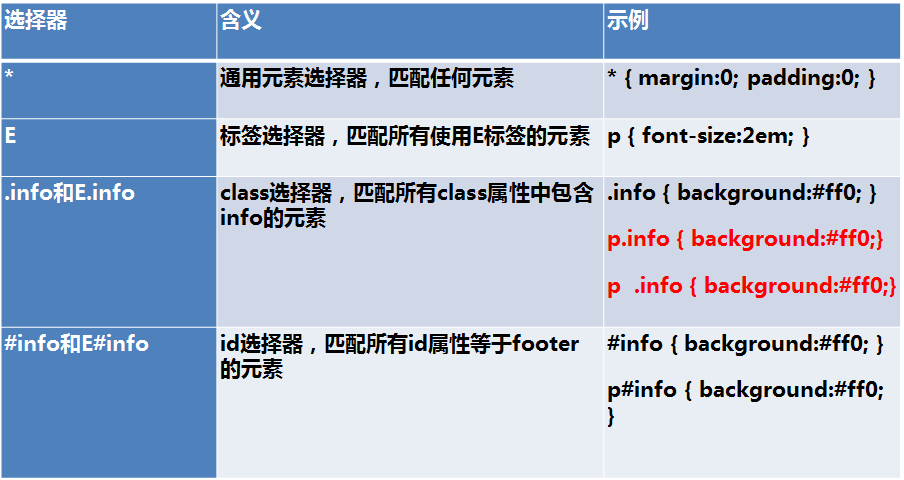
红色字体中选择器的区别是:p.info的意思是p元素中必须有class="info"属性将被选择,p .info是选择后代元素,示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
p.info {
color: red;
}
p .info {
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>选择器</h2>
<p class="info">p1</p>
<p>
<span class="info">span1</span>
<p>p3</p>
</p>
</body>
</html>显示结果为:

-
组合选择器
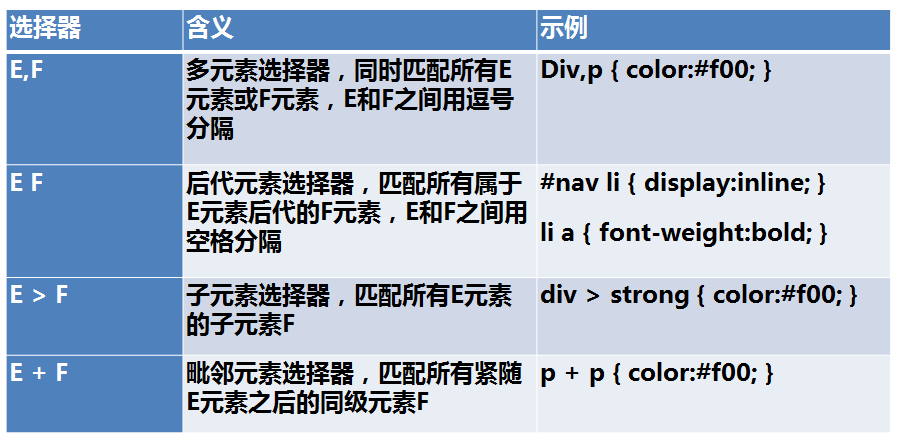
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>组合选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
#div1 span {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>组合选择器</h2>
<div id="div1">
<span>span1</span>
<div id="div2">
<span>span2</span>
</div>
</div>
<span>span3</span>
</body>
</html>显示效果:

示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>组合选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
#div1>span {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>组合选择器</h2>
<div id="div1">
<span>span1</span>
<div id="div2">
<span>span2</span>
</div>
</div>
<span>span3</span>
</body>
</html>显示效果:

实例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>组合选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
#div1+span {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>组合选择器</h2>
<div id="div1">
<span>span1</span>
<div id="div2">
<span>span2</span>
</div>
</div>
<span>span3</span>
<span>span4</span>
</body>
</html>显示效果:

-
属性选择器
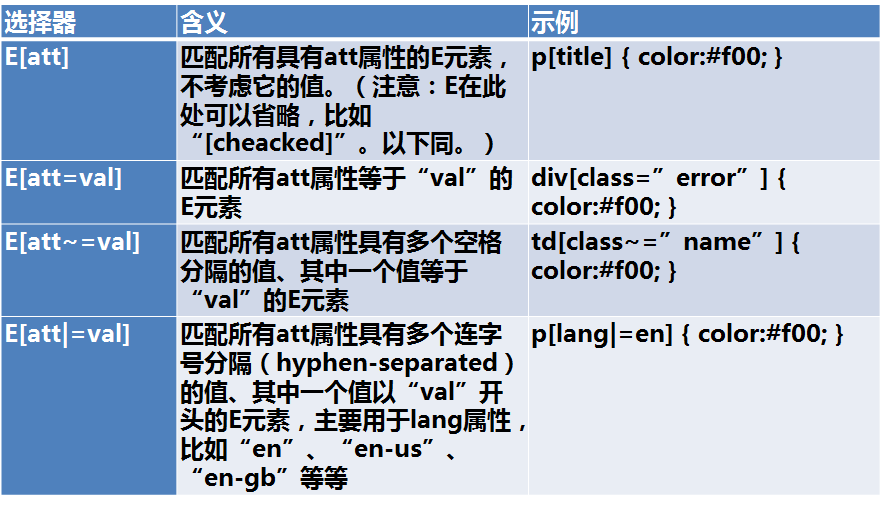
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
div[id][class~=cls1] {
background: lightgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>组合选择器</h2>
<span>span0</span>
<div id="div1" class="cls1">
div1
</div>
<div id="div2" class="cls1 cls2">
div2
</div>
</body>
</html>显示效果:

-
伪类
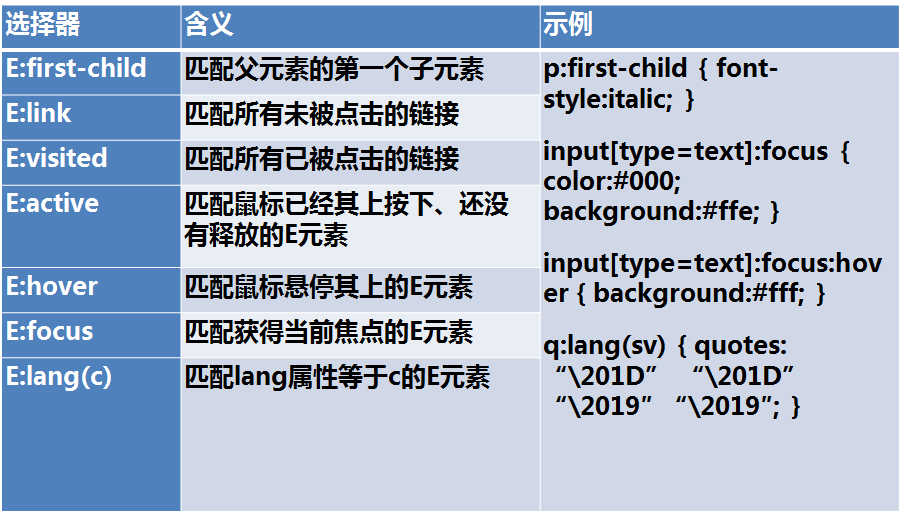
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪类</title>
<style type="text/css">
td:first-child {
background: lightcoral;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>组合选择器</h2>
<table border="1" width="100%">
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
</table>
<hr />
<table border="1" width="100%">
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
<td> </td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>显示效果:
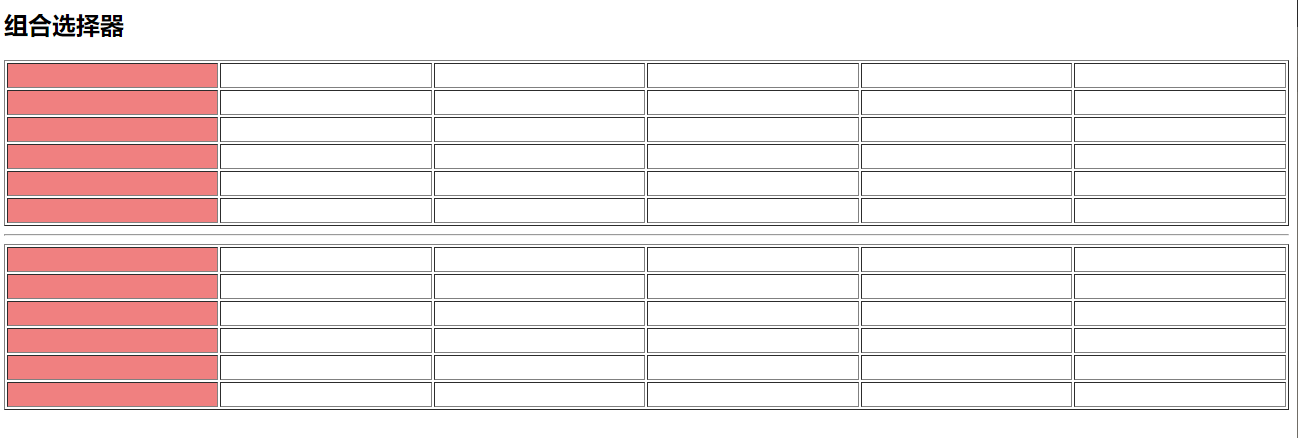
练习:实现隔行换色,当鼠标悬停在每一行上时高亮显示为黄色,按下时高亮红色。
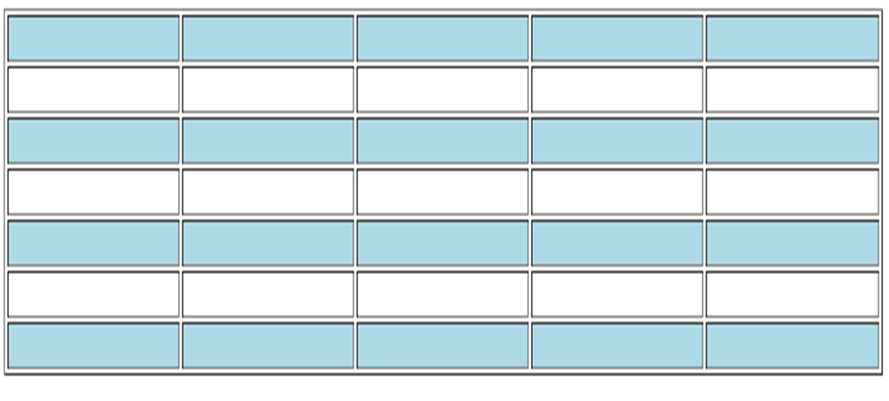
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13<style type="text/css">
tr:nth-child(2n+1) {
background: lightblue;
}
tr:hover {
background: yellow;
}
tr:active {
background: orangered;
}
</style> -
伪元素
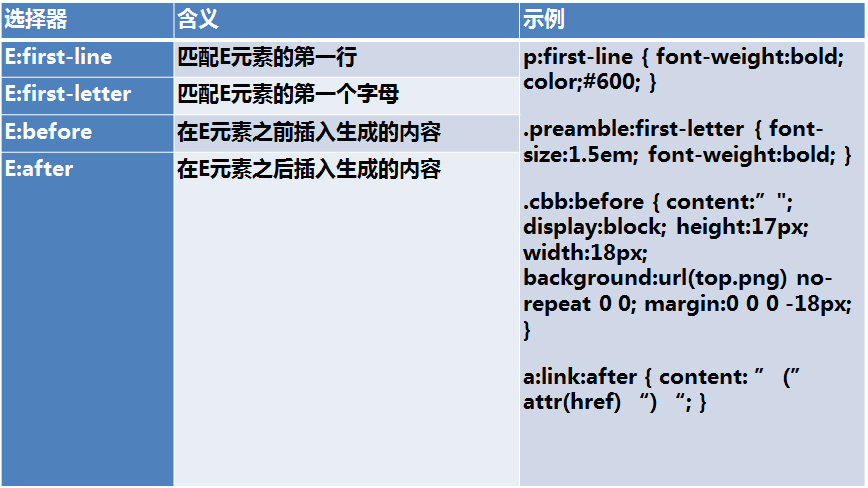
标准的伪元素应该使用::,但单:也行,只是为了兼容。
示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪类</title>
<style type="text/css">
a::before {
content: "网站";
display: inline-block;
background: red;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>伪元素</h2>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度</a>
<a href="http://best.cnblogs.com">博客园</a>
</body>
</html>显示效果:

content的特殊值
- none:不生成任何内容
- attr:插入标签属性值
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪元素</title>
<style type="text/css">
a:before {
content: attr(title);
}
a:after {
content: attr(href);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>我喜欢的网站</h2>
<a href="http://www.cnblogs.com" title="技术">博客园</a>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" title="国内">百度</a>
<a href="http://www.google.com" title="国外">谷歌</a>
</body>
</html>显示效果:

url:使用指定的绝对或相对地址插入一个外部资源(图像,声频,视频或浏览器支持的其他任何资源)
示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪元素</title>
<style type="text/css">
a:before {
content: url(../img/success.png);
}
a:after {
content: url(https://ss0.bdstatic.com/5aV1bjqh_Q23odCf/static/superman/img/logo/bd_logo1_31bdc765.png);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>我喜欢的网站</h2>
<a href="http://www.cnblogs.com" title="技术">博客园</a>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" title="国内">百度</a>
<a href="http://www.google.com" title="国外">谷歌</a>
</body>
</html>显示效果:

string:插入字符串;插入的伪元素可以作为一个元素使用,元素是被插入在指定元素内部,是父子关系:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪元素</title>
<style type="text/css">
#div1 {
background: red;
}
#div1:before {
content: " ";
display: block;
background: lightgreen;
border-radius: 50px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
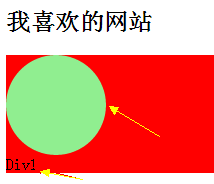
<h2>我喜欢的网站</h2>
<div id="div1">
Div1
</div>
</body>
</html>显示效果:
特殊性(优先级)
- 优先级
- 同类型,同级别的样式后者先于前者
- ID > 类样式 > 标签 > *
- 内联>ID选择器>伪类>属性选择器>类选择器>标签选择器>通用选择器(*)>继承的样式
- 具体 > 泛化的,特殊性即css优先级
- 近的 > 远的 (内嵌样式 > 内部样式表 > 外联样式表)
内嵌样式:内嵌在元素中,<span style=“color:red”>span</span>
内部样式表:在页面中的样式,写在<style></style>中的样式
外联样式表:单独存在一个css文件中,通过link引入或import导入的样式 - !important 权重最高,比 inline style 还要高
示例:显示效果:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>优先级</title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
color: yellow;
}
p {
color: red ;
}
.cls1 {
color: deeppink;
}
.cls2 {
color: blueviolet;
}
#p1 {
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p id="p1" class="cls2 cls1" style="color:#ccc">p1</p>
<span>span1</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
- 计算特殊性值
-
important > 内嵌 > ID > 类 > 标签 | 伪类 | 属性选择 > 伪对象 > 继承 > 通配符
-
权重、特殊性计算法:
CSS样式选择器分为4个等级,a、b、c、d- 如果样式是行内样式(通过Style=“”定义),那么a=1,1,0,0,0
- b为ID选择器的总数 0,1,0,0
- c为属性选择器,伪类选择器和class类选择器的数量。0,0,1,0
- d为标签、伪元素选择器的数量 0,0,0,1
- !important 权重最高,比 inline style 还要高
比如结果为:1093比1100,按位比较,从左到右,只要一位高于则立即胜出,否则继续比较:
{% asset_img pic-26.png 特殊性值 %}示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>优先级</title>
<style type="text/css">
html body #div1 {
background: red;
}
.cls1 #div1 {
background: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="cls1">
<div id="div1">div1
</div>
<div id="div2">div2
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>显示结果:
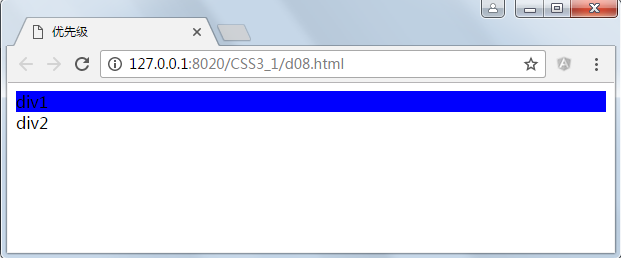
因为html body #div1的特殊性值为:0102,而.cls1 #div1的特殊性值为0110,后者胜出。
刻度
在CSS中刻度是用于设置元素尺寸的单位。
特殊值0可以省略单位。例如:margin:0px可以写成margin:0
一些属性可能允许有负长度值,或者有一定的范围限制。如果不支持负长度值,那应该变换到能够被支持的最近的一个长度值。
长度单位包括包括:相对单位和绝对单位。
相对长度单位包括有: em, ex, ch, rem, vw, vh, vmax, vmin
绝对长度单位包括有: cm, mm, q, in, pt, pc, px

-
绝对长度单位
1in = 2.54cm = 25.4 mm = 72pt = 6pc = 96px -
文本相对长度单位
em
相对长度单位。相对于当前对象内文本的字体尺寸。如当前对行内文本的字体尺寸未被人为设置,则相对于浏览器的默认字体尺寸。(相对父元素的字体大小倍数)
body { font-size: 14px; }
h1 { font-size: 16px; }
.size1 p { font-size: 1em; }
.size2 p { font-size: 2em; }
.size3 p { font-size: 3em; }
浏览器的默认字体大小为16像素,浏览器默认样式也称为user agent stylesheet,就是所有浏览器内置的默认样式,多数是可以被修改的,但chrome不能直接修改,可以被用户样式覆盖。
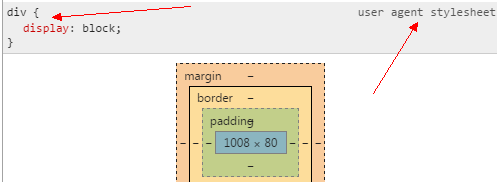
示例:
1 |
|
显示结果:
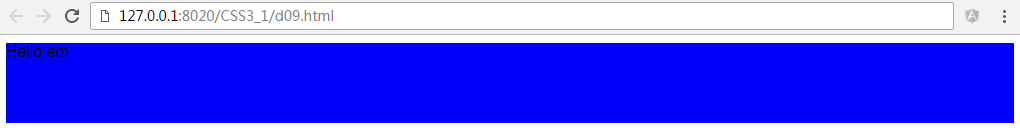
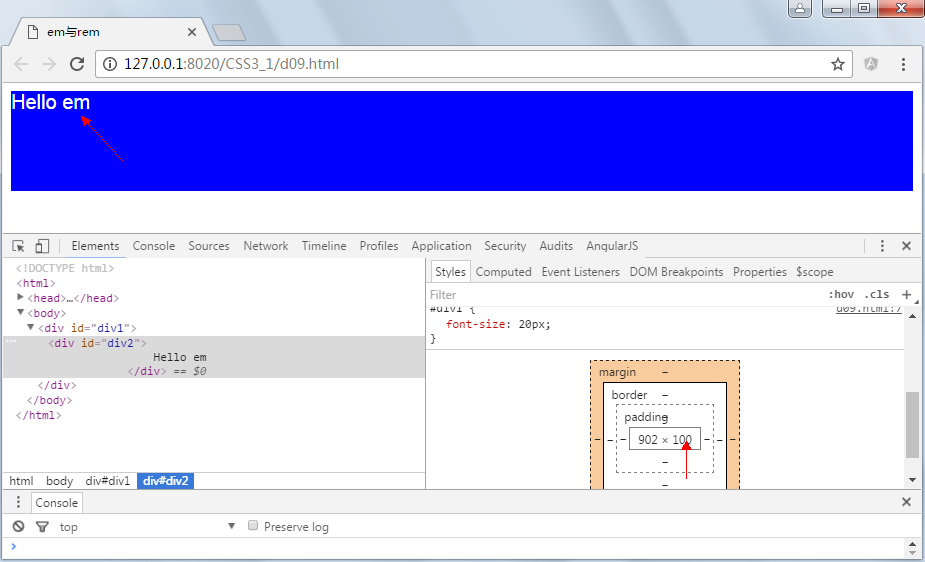
div2的高度为80px,是因为user agent stylesheet默认样式中字体大小为16px,按照这个规则我们可以手动修改字体大小,div2的高度将发生变化。
示例:
1 |
|
显示结果:
rem
- rem是CSS3新增的一个相对单位(root em,根em),相对于根元素(即html元素)font-size计算值的倍数
- 只相对于根元素的大小
rem(font size of the root element)是指相对于根元素的字体大小的单位。简单的说它就是一个相对单位。看到rem大家一定会想起em单位,em(font size of the element)是指相对于父元素的字体大小的单位。它们之间其实很相似,只不过一个计算的规则是依赖根元素一个是依赖父元素计算。(相对是的HTML元素的字体大,默认16px)
示例:
1 |
|
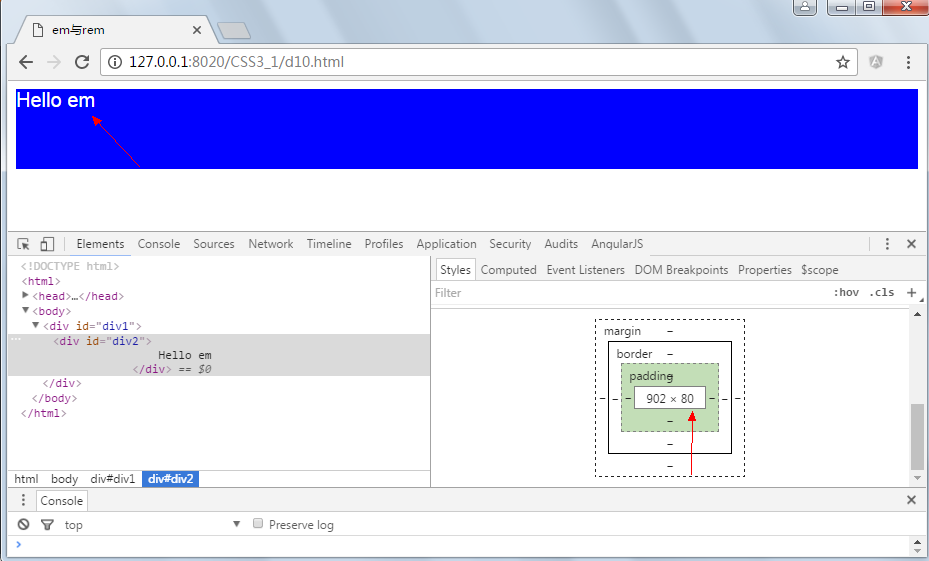
显示结果:
示例:
1 |
|
显示结果:
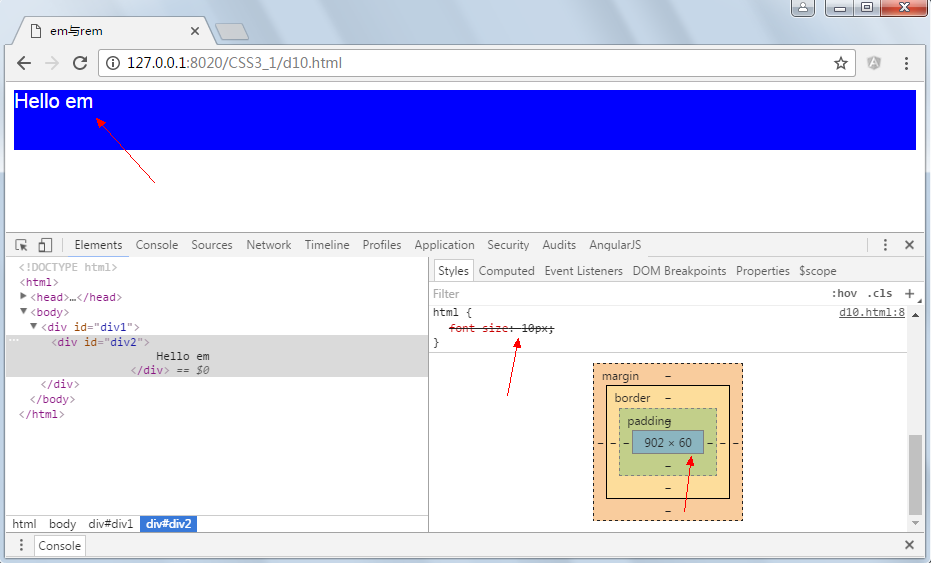
按理说高度为5*10px=50像素高度,但这里为60,是因为chrome浏览器限制了最小字体大小为12px,从上图可以看出。
- Web App与Rem
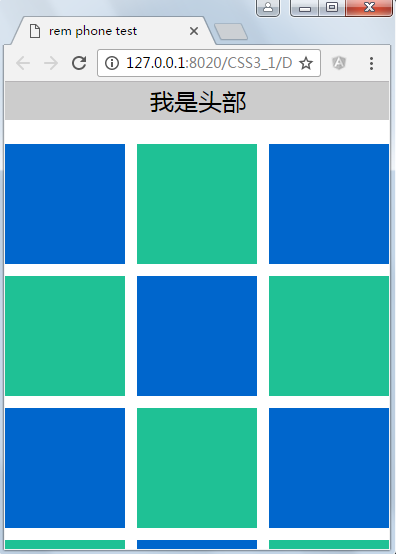
为了实现简单的响应式布局,可以利用html元素中字体的大小与屏幕间的比值设置font-size的值实现当屏幕分辨率变化时让元素也变化,以前的tmall就使用这种办法,示例如下:

示例一:
1 |
|
显示结果:

示例二:
1 | <html> |
显示结果:
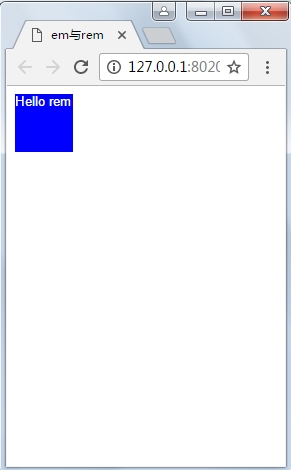
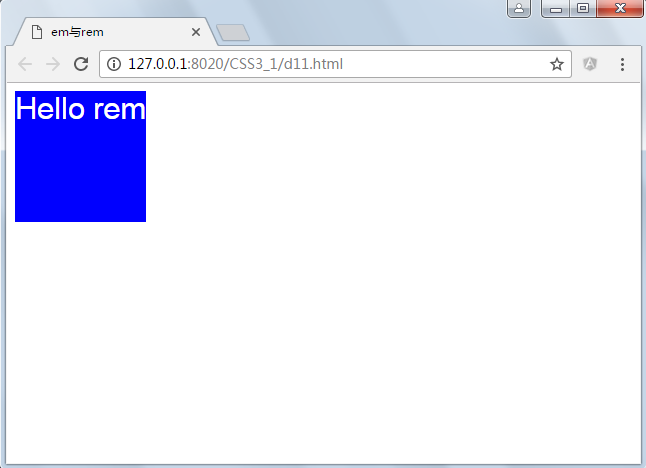
变屏幕变宽时元素大小也随之发生变化,但这里并没有考虑高度,但为响应式布局与hack提供了思路。
示例与帮助下载
请访问原始作者Github
视频下载
原始作者留下的视频链接,未曾访问
作业
- 请完成所有上课示例
- 请完成下面的手机页面,当浏览器大小变化时图片与字体的大小发生变化,图标请使用字体图标,注意设定一个下限与上限值